华清远见 实习面试题
描述有哪些段
Code:代码段,存放程序代码RO-data:只读数据段,存放程序中定义的常量RW-data:读写数据段,存放初始化为非0的全局变量ZI-data:数据段,存放未初始化的全局变量及初始化为0的变量
int const *p, int *const p, int *const *p的区别
int const *p 表示*p的值不能改变,而p是可以改变的,即地址变量可以指向新的地址,但是指向的变量的值是不可以改变的。
int *const p 表示*p的值可以改变,而p是不可改变的,即地址变量不可以指向新的地址,但是指向的变量的值是可以改变的。
int *const *p 表示*p的值不能改变,而p也是不可以改变的,即地址变量不可以指向新的地址,并且指向的变量的值也是不可以改变的。
简述UART和SPI的区别
UART
- 全双工通讯
- 异步通讯
SPI
- 全双工通讯
- 串行同步通讯
实现strcmp()函数,不能调用其他的库函数
int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2)
{
while (*s1 == *s2)
{
if (*s1 == '\0')
{
return 0;
}
s1++;
s2++;
}
if (*s1 > *s2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
将链表逆序输出,不可以使用其他的
题目前提条件:
typedef struct _node {
struct _node *next;
int vaule;
}Node;
Node head;
使用双指针法逆序单向链表:
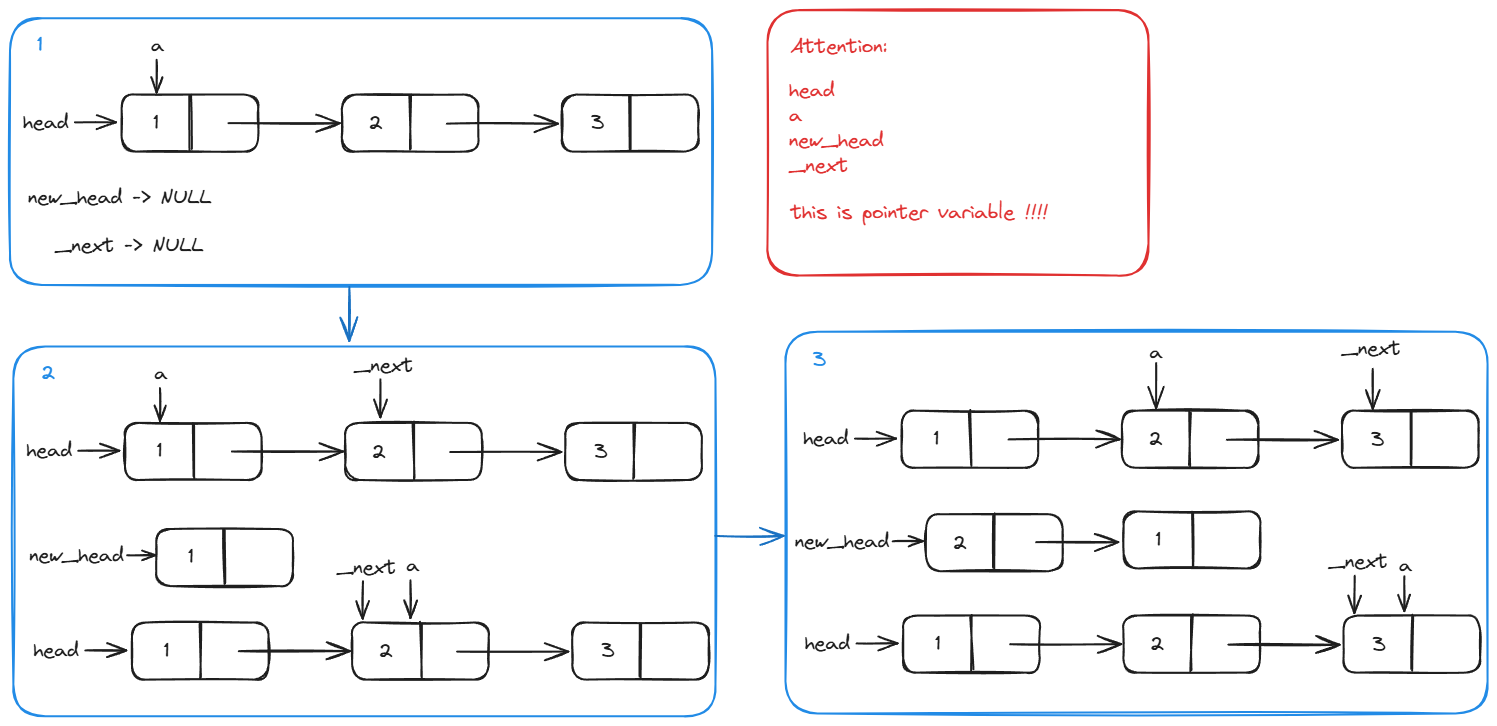
// 默认这个单向链表是一个不带头节点的单向链表
int reversed_list(Node *head)
{
Node *_next;
Node *a = head;
Node *new_head = NULL;
while (a != NULL)
{
_next = a->next;
a->next = new_head;
new_head = a;
a = _next;
}
head = new_head;
return 0;
}
编写程序区分机器是大端还是小端
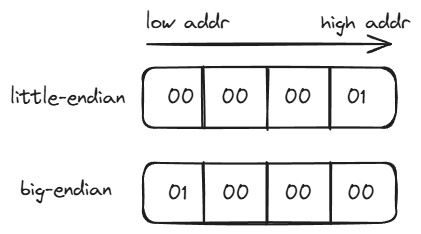
-
声明一个
int变量,赋值为1,再将其第一个byte取出来,判断是为1bool IsBig_Endian(void)
{
unsigned int test = 1;
if( *((unsigned char *)&test) == 1)
{
return true;
}else
{
return false;
}
} -
使用联合体判断
bool IsBig_Endian(void)
{
union {
unsigned int i;
unsigned char s[4];
}c;
c.i = 1;
return (c.s[0] == 1);
}